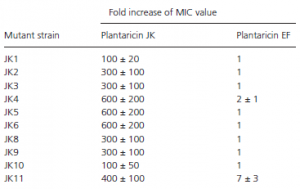
The bacterial strains that are resistant to the two -peptide bacteriocin (antimicrobial peptide) plantaricn JK. It has been shown that resistance occurred due to mutations in a gene encoding an APC superfamily protein with 12 transmembrane helices. The genome was sequenced.
The specificity of the mutant strains was tested by determining how the sensitivity to plantaricin EF (a two-peptide bacteriocin that is very different from plantaricin JK) was affected. The results revealed that there was no significant reduction in the sensitivity of the mutants to plantaricin EF, whcih indicates that the increased resistance of the mutants to plantaricin JK is not a general effect on bacteriocin resistance, but an effect that is specific for plantaricin JK.
See reference:
Camilla Oppegård, Morten Kjos, Jan-Willem Veening, Jon Nissen-Meyer, and Tom Kristensen. A putative amino acid transporter determines sensitivity to the two-peptide bacteriocin plantaricin JK. 2016. Microbiology Open.